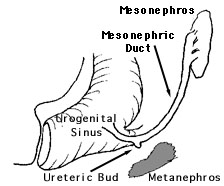
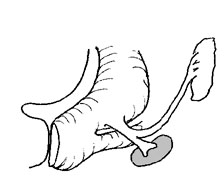

The mesonephric (Wolfian) duct descends from the mesonephros to meet the urogenital sinus. Once this connection is made, fetal urine drains into the urogenital sinus. The ureteric bud arises from the mesonephric duct and progresses laterally to invade the metanephrogenic blastema (precursor of the mature kidney). The caudal end of the mesonephric duct (past the ureteric bud is called the common excretory duct. As renal development proceeds, the common excretory duct is incorporated into the urogenital sinus. Progressive incorporation of the common excretory duct eventually leads to separate openings of the ureter and mesonephric duct into the urogenital sinus. By 37 days of gestation, the ureter empties into the urogenital sinus cephalad to the mesonephric duct. The urogenital sinus is divided between the orifices of these two tubes. The cephalad portion of the urogential sinus will become the bladder while the caudal portion will become the urethra.



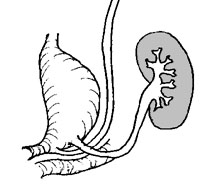
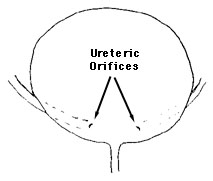
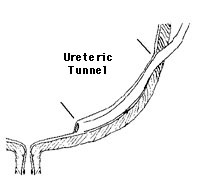
The caudal end of the developing bladder thickens with smooth muscle in a triangle between the two ureteric orifices and the urethra, the trigone.
See Abnormal Bladder Development.
Return to G/U Development Home Page
©David A. Hatch, M.D., 1996