Ascites
What are the options for imaging procedures for evaluating ascites?
- US
- CT
Which is the imaging procedure of choice in a suspected case of ascites?
- Smaller amounts of ascites are best imaged with ultrasound and CT.
Image Atlas for Ascites
What are the radiological findings of ascites in plain radiographs?
Only large amounts of intra peritoneal fluid can be detected on the plain abdominal film.
- The fluid causes a generalized haziness or "ground glass" appearance to the abdomen.
- The bowel loops may be separated by interposed fluid and bowel loops assume a central location as they float to the highest point of the abdomen.
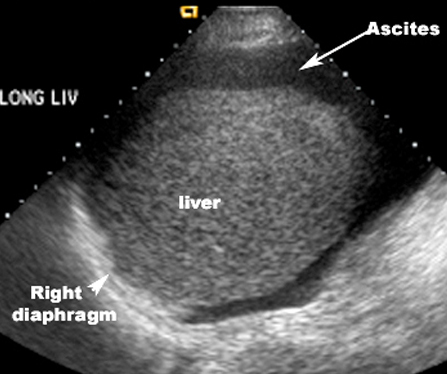
Imaging findings of ascites in ultrasound and CT:
- Ascites is seen as an anechoic space on ultrasound.
- Ascites is seen as low density collection surrounding the bowel in CT.
- Bowel loops float anteriorly.
- Ascites is seen earliest in the pelvis due to its dependent position in the recto vescical or vagino vescical pouch..
- Next it accumulates in the sub hepatic region, in the Morrison's pouch.
US
-
Ascites appears echo free (black).
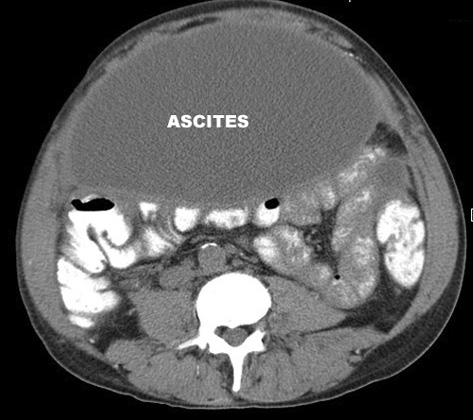
Loculated Ascites
- In infectious or malignant conditions the ascites may be loculated, with enhancement of the peritoneum on post-contrast study.
- The presence of soft tissue masses on CT, in association with ascites, may be a clue as to a malignant etiology.
CT
- Large loculated ascites
- low density collection,
- displacing bowel posteriorly
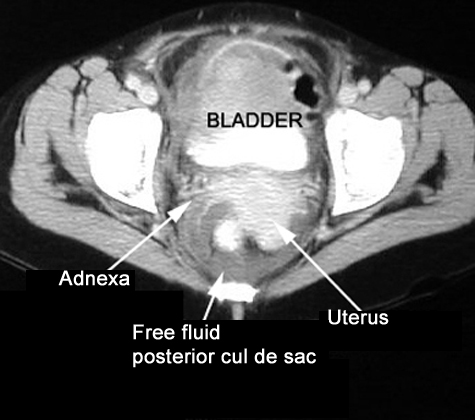
CT
-
Free fluid in the posterior cul de sac