Diffusion
Objectives
68 year old female with dyspnea at rest for 5 years.
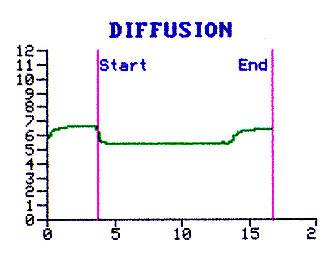
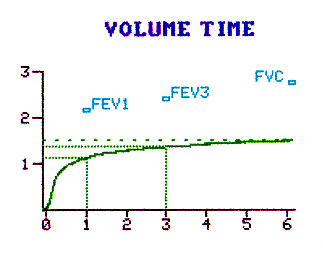
Diffusion defect is considered present when the % predicted diffusion is less than 75%.
The 2 std deviation for normal range is 25%.
Our patient has diffusion of %, hence has a diffusion defect.
Severity of diffusion defect:
Our patient's diffusion is % of predicted. The diffusion defcet is .
Variables causing diffusion defect:
|
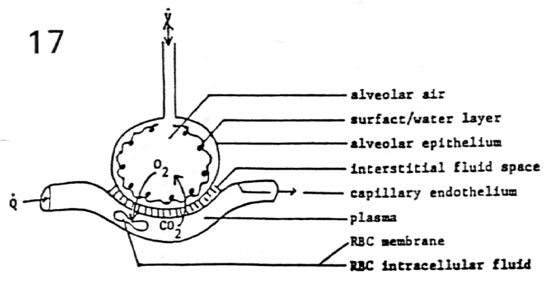 |
The primary object of performing the test is to identify alveolar capillary membrane thickness. We have to find ways to make corrections for other variables.
In our patient the low diffusion is not corrected by Hemoglobin, there is no obstruction to consider V/Q mismatch and diffusion is low even when expressed by DL/VA. Hence the low diffusion in this patient is due to alveolar capillary membrane thickness.
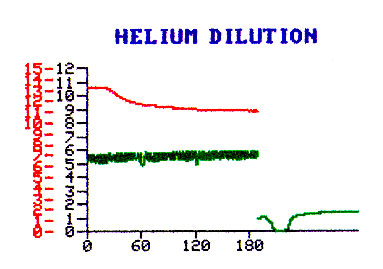
| In performing DLCO we ask the patient to inhale an air mixture containing
Carbon monoxide and Helium. Helium is to obtain the alveolar surface area for that breath
(single breath TLC). Patient is expected to hold the breath for 10 seconds and exhale.
Technician collects the terminal portion of exhalation (alceolar air) and measures the
carbon monoxideconcentration. A complex formula is then used tio calculate DLCO and VA
BTPS. You find out the current Hemoglobin to make the necessary correction. In evaluating the graph note the depth of inhalation, duartion of breath holding and the timing of collection of alveolar air. |
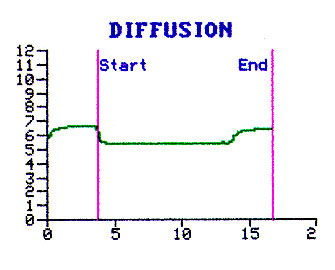 |
Our patient has performed the test satsfactorily.