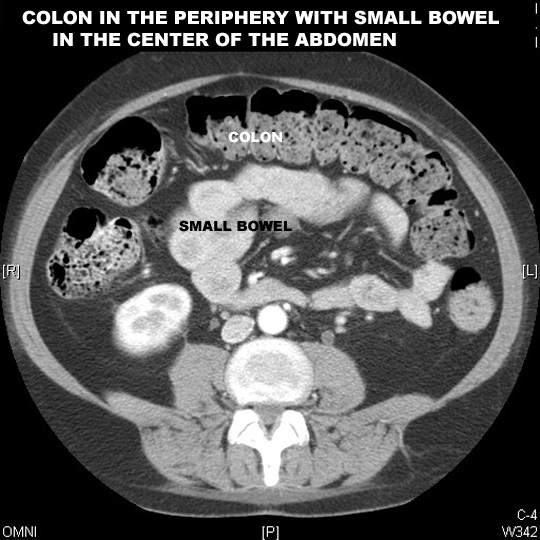
 |
Normal Bowel
|
Dilated bowel which may be from:
How do you distinguish small from large bowel?
 |
Normal Bowel
|
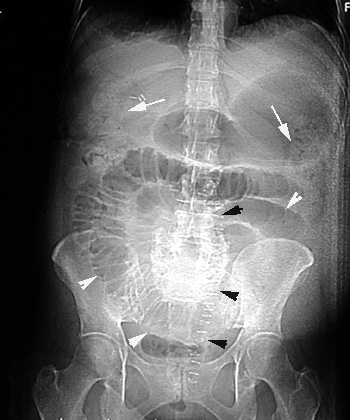 |
Plain film in a case with Small bowel obstruction
|
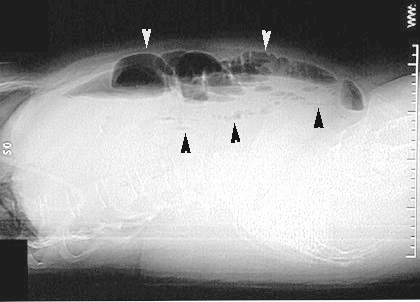 |
Small bowel obstructionCross lateral view shows multiple dilated fluid filled loops of bowel with air fluid levels. |
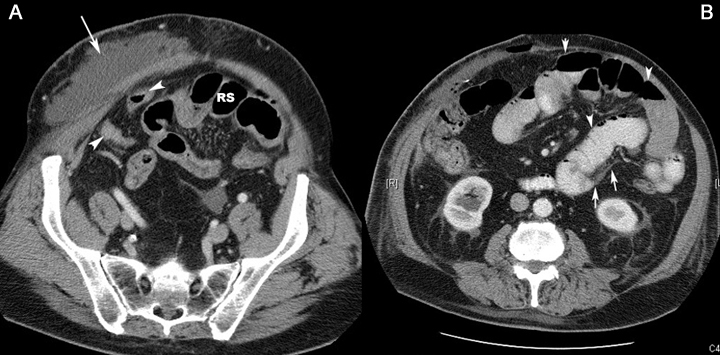 |
CT scan of another patient showing
findings of small bowel obstruction:
|
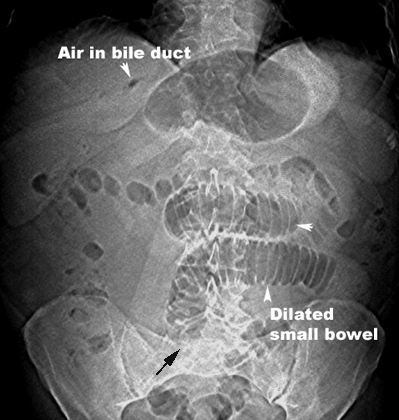 |
Gall stone Ileus
|
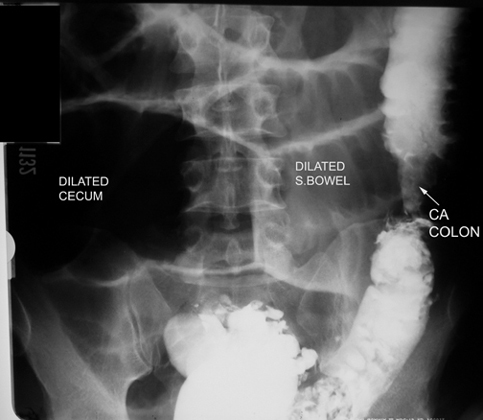 |
Lower GI in a patient with Large bowel Obstruction
|