Abdominal Abscess
Collection of pus
It can be in any organ or abdominal cavity based on the etiology.
What are the common sites of abscess?
- Post-op
- Subdiaphragmatic
- Appendiceal
- Diverticulitis
- Pancreatitis
- Liver abscess
- Renal abscess
What are the useful imaging procedures in the evaluation of abdominal abscess?
- CT abdomen is the imaging procedure of choice in evaluating patients suspected to have abdominal abscess.
- US and CT can guide placement of drainage of abscess.
- Plain abdomen radiographs can detect abdominal abscesses, but of low sensitivity. Extraluminal air pockets can be recognized.
What are the imaging findings of abdominal abscess?
- Abnormal fluid collection, usually with air seen outside the lumen of the bowel.
- Periphery may enhance with intravenous contrast material.
Image Atlas of Intra-abdominal Abscess
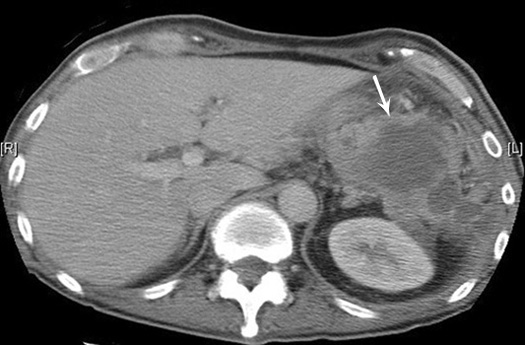
Post op
Subdiaphragmatic abscess post splenectomy
- Arrow points to multiloculated thick walled fluid collection in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen.
- Note absence of spleen.
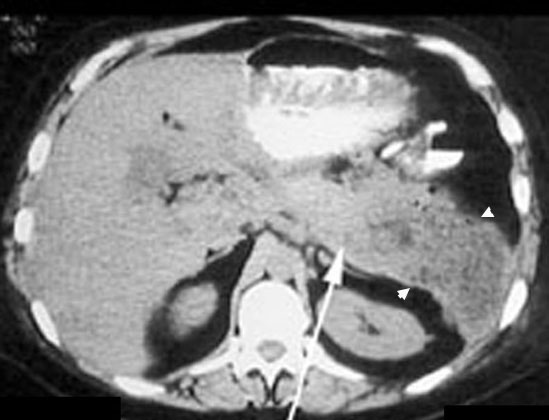
Pancreatic abscess
Acute Pancreatitis
- Diffusely enlarged pancreas with air pockets.
- Arrow points to body of pancreas.
- Abscess is in tail of pancreas.
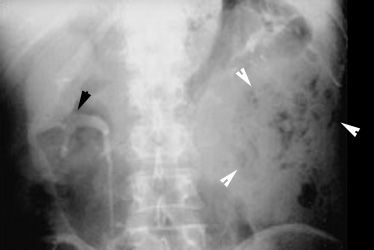
Renal abscess
- 40 year old man with fever and diarrhea for two weeks. He has infected urine.
- IVP shows functioning right kidney (black arrowhead).
- No function in the left kidney.
- Air pockets seen in the left flank (white arrowheads).
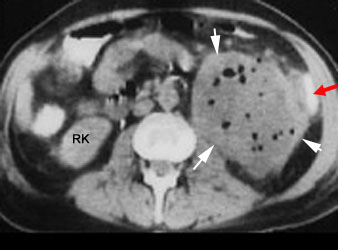
Renal abscess
CT shows a large mass in the left renal area with multiple air pockets and absence of functioning renal parenchyma.
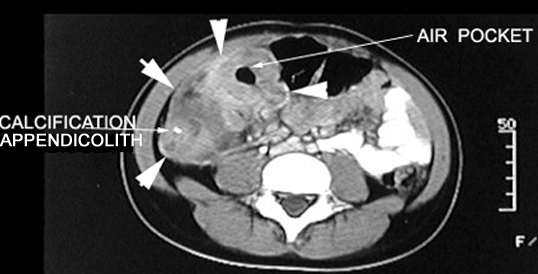
Acute Appendicitis
Appendiceal abscess
CT Post-contrast:
- Arrows point to the inflammatory mass in the right lower quadrant with an air pocket indicating an abscess.
- Mass demonstrates contrast enhancement.
- Calcification seen within the mass probably represents an appendicolith.