| Pathology |
| Aliya N. Husain, M.D. |
 |
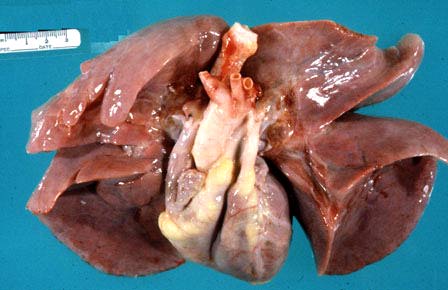
| Gross photograph of normal lungs and heart. The pleural surface is smooth and shiny. The lungs extend down to the apex of the heart. |
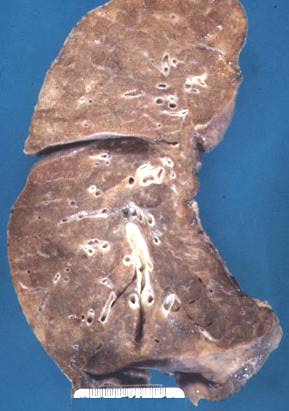 |
| Cut surface of normal lung. |
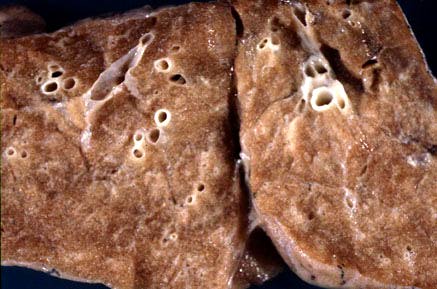 |
| Cut surface of normal lung (same as in fig. 2). |
 |
| Right main bronchus is longer and more in line with the trachea (gross photograph, posterior view). |
 |
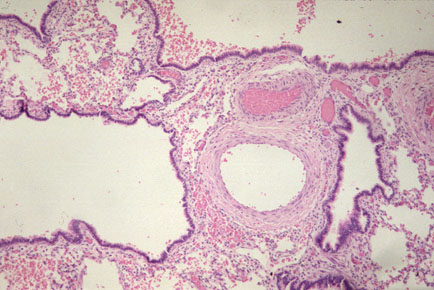
| Microscopic section of normal bronchus showing respiratory epithelium, submucosal glands and cartilage. |
 |
| High power of fig. 6, with pseodostratified respiratory epithelium at top and cartilage at bottom. |
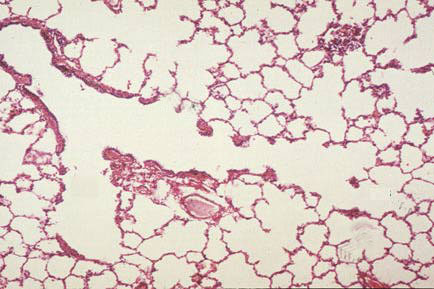 |
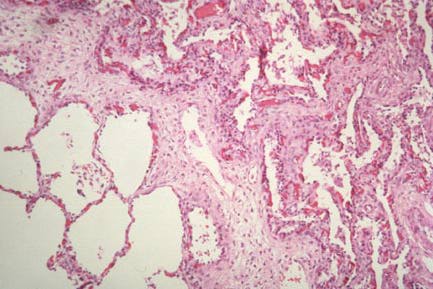
| Microscopic section of normal lung showing terminal bronchiole, respiratory bronchiole, alveolar duct, alveolar sac, and alveoli. |
 |
| High power of normal alveoli. |
 |
| Electron micrograph of type II pneumocyte with nucleus in upper right corner and lamellar body (surfactant) in middle. |
 |
| Red, consolidated and hypocrepitant lungs in hyaline membrane disease (HMD) (gross picture). |
 |
| Low power photomicrographic of HMD showing immature lung with hyaline membranes. |
 |
| High power showing eosinophilic (pink) acellular hyaline membrane lining air spaces. |
 |
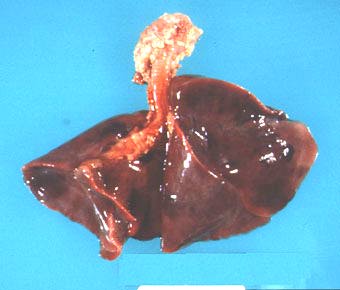
| Gross photograph of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). There is irregular scarring with depressed and hyperinflated areas. |
 |
| Low power of lung with BPD; severe fibrosis at upper left, compensatory emphysema of less damaged area at bottom right. |
 |
| Post-surfactant BPD with less fibrosis and arrest in lung development resulting in fewer though larger alveoli. |
 |
| X-ray of patient with left-congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH), after barium meal. |
 |
| Severe pulmonary hypoplasia, more marked on left, in patient with left CDH. As compared to the heart, the lungs are extremely small. |
 |
| Gross photograph of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM) type I. There is one large predominating cyst filled with mucin. |
 |
| Microscopic picture showing respiratory type epithelium living cyst in CCAM, type I. |
 |
| CCAM, type II, intrapperative picture showing multiple cyst. |
 |
| CCAM, type II, cut surface of lung showing multiple small cysts. |
 |
| Microscopic picture of CCAM, type II, with cysts lived by ciliated epithelium. |
 |
| High power of fig. 23, showing living epithelium of cyst in CCAM, type II. |
 |
| Low power photomicrograph of adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) showing hyaline membranes and interstitial edema. |
 |
| High power of fig. 25, acute ARDS. |
 |
| Cut surface of normal lung, though edemetous for comparison with fig. 28. |
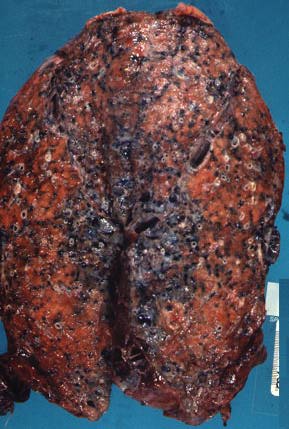 |
| Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, cut surface of lung with fibrosis and antheacosis. |