 |
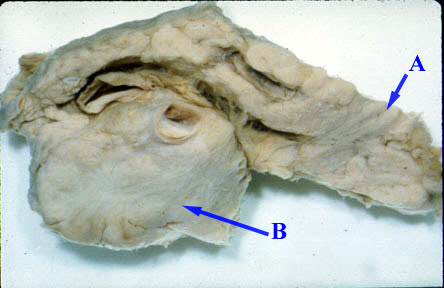
The pancreas is bisected along its longitudinal axis revealing a large adenocarcinoma (B) of the head. (A) is the tail of pancreas which is normal. |
 |
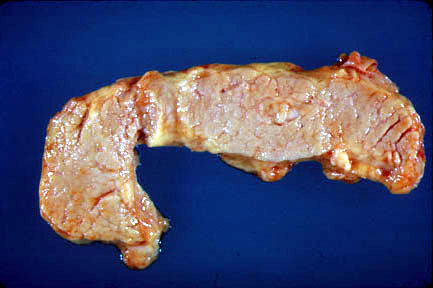
The normal pancreas is gray-yellow to tan throughout the organ |
| Test | Sensitivity | Specificity |
| Ultrasound | 80 | 90 |
| Endoscopic US | 90 | 90 |
| CT scan | 90 | 95 |
| Retrograde cholangiopancreatography | 90 | 90 |
| MRI scan | 90 | 90 |
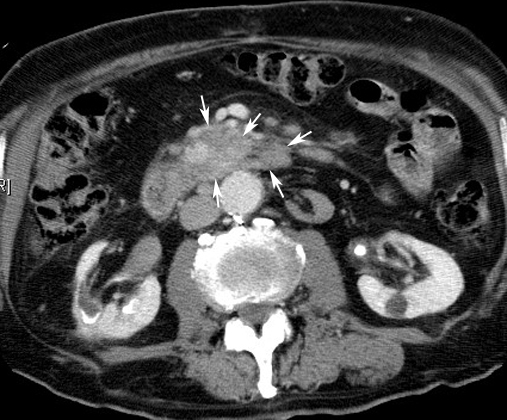 |
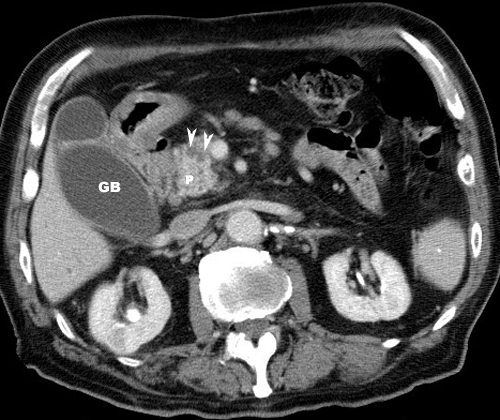
carcinoma pancreasArrows: Note enhancing mass head of pancreas extending medially into the uncinate process. |
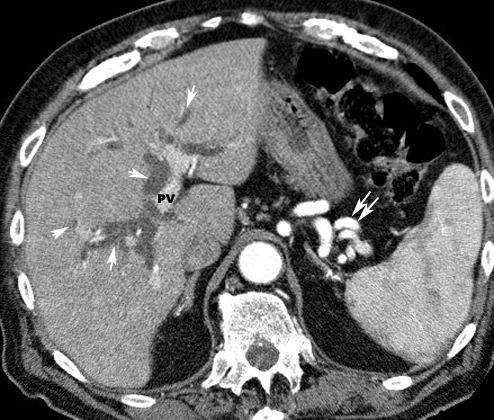 |
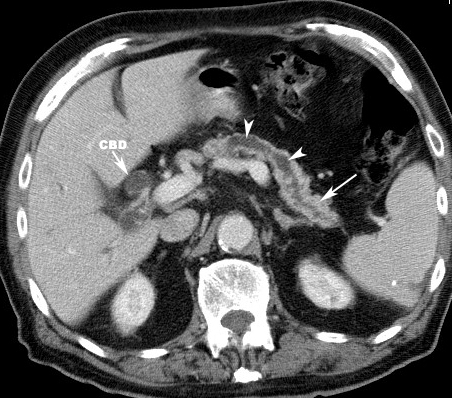
carcinoma pancreasArrows point to dilated intrahepatic bile ducts indicating obstructive jaundice. Bile ducts are next to contrast filled branches of the portal vein (PV) Double arrows point to peri splenic varicocities. |
 |
carcinoma pancreas
|
 |
carcinoma pancreas
|
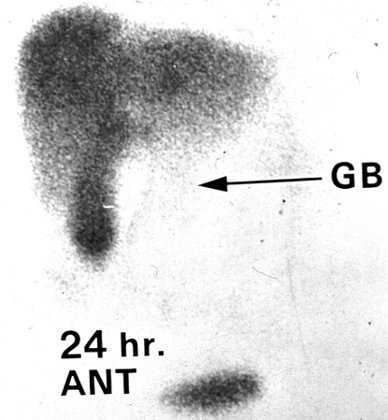 |
Courvoisier gallbladderThe liver and a distended gallbladder are seen in this nuclear medicine study isotope. However, no excretion of the isotope into the bowel is seen indicating a complete obstruction of the common bile duct. Isoptope has been taken up by the liver parenchyma and with excretion into GB indicating patent cystic duct. But there is no spill into the duodenum which indicates common bile duct obstruction
|