Mammography
What are the common clinical problems presenting as breast mass?
Common breast masses are:
- Cyst
- Fibroadenoma
- Cancer
What is the utility of the following imaging studies in the evaluation of breast mass?
- Mammography
- Ultrasound
- CT
- MR
- Thermography
- Is the imaging technique of choice for investigation of any palpable breast mass?
- Mammography is the gold standard imaging procedure for detection of early cancer.
- It is complementary to physical examination.
- Each method can detect tumors not detected by the other.
- Useful to guide diagnostic procedures.
Ultrasound
- Is useful to distinguish a cyst from a solid mass and should not be relied for cancer screening.
- There is increasing use of ultrasound as a supplemental procedure following mammography to evaluate breast masses.
- Useful to guide diagnostic procedures.
CT, Nuclear medicine scans and Thermography have no significant role in the evaluation of breast masses as of now.
MR: New developments in evaluating the utility of this imaging modality is on going.
How is mammography done? What are the views?
Answer
- Cranio-caudal (top to bottom) view
- Medio-lateral oblique views: (MLO) for better visualization of tail of breast
- "Spot" views and magnification views can sometimes be used as well.
What is the primary utility of mammogram?
Answer
- The primary purpose of mammogram is to detect breast cancers.
- It is useful in the evaluation of palpable breast mass.
- It is a useful to guide diagnostic procedures.
How does mammogram differ with age?
Answer
- In young women, the breast may be dense.
- As women age there is fatty infiltration of the breast associated with atrophy of glandular tissue.
- Fat is lucent and is dark in mammogram.
- Glandular tissue and cancer are dense and white in mammogram.
- Hence, it is difficult to distinguish cancer from normal dense glandular tissue in young women but fatty breast forms a good contrast for Cancer.
What are the primary and secondary mammographic signs of malignancy?
Answer
- Primary:
- Mass
- A spiculated mass is a common mammographic appearance.
- Calcifications
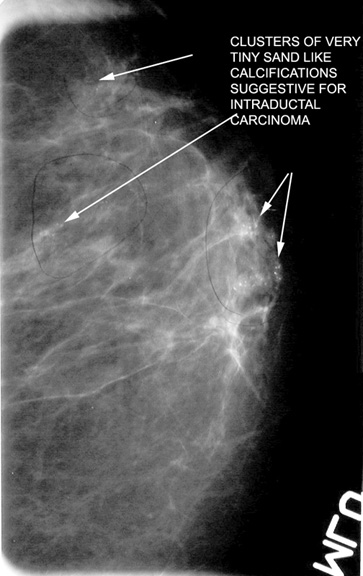
- Micro calcifications may be seen on mammography in at least 30% of cases of invasive carcinoma.
- They are 1 mm or less and sand-like.
- The calcifications may represent necrotic debris.
- Developing density
- Mass
Secondary:
- Architectural distortion
- Skin thickening or retraction
- Nipple and areolar thickening
- Abnormal ductal patterns
- Lymphadenopathy
- Asymmetry of the breast tissue
What is the most common type of breast cancer?
Answer
- 65-80% Invasive ductal carcinoma arises from the epithelium of the breast ducts.
- 03-14% Lobar carcinoma Invasive lobular carcinoma arises from the acini of breast lobules.
- 02-08% Tubular carcinoma
- Less than 1% of invasive breast cancers are sarcomatous or other mesenchymal origin.
What are the mammographic findings of invasive ductal carcinoma?
Answer
- Irregular mass
- New calcifications
- Calcifications are sand like
What are the mammographic findings of invasive lobar carcinoma?
Answer
- Increased density, mass
What is the role of radiologist in biopsy of breast mass?
Answer:
- Core biopsy with stereotactic or ultrasound guidance.
- The lesion can be localized by the radiologist for biopsy and/or resection with mammographic or ultrasound guidance.
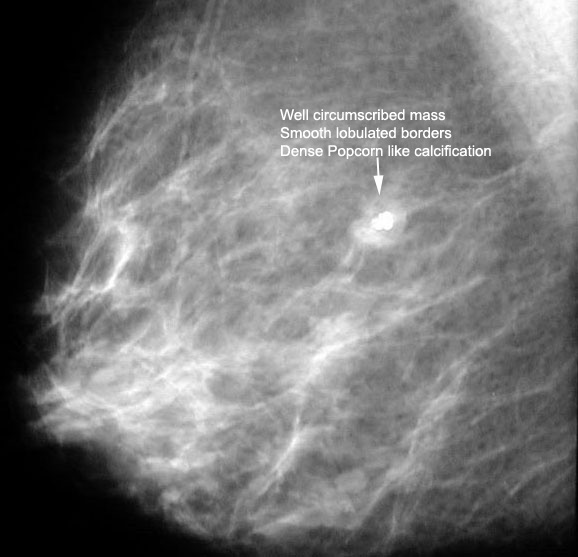
What is the classical appearance of fibroadenomas on mammography?
Answer:
- A fibroadenoma appears as a well-circumscribed round or oval mass with well-defined borders.
- They may be multiple and bilateral.
- It may have the appearance of a dense, popcorn-like calcification on mammogram.
What is the most effective modality for the detection of breast cancer ?
- Clinical breast exam
- MRI
- Mammography
- Ultrasound
Answer
- Mammography
While all of the above modalities can potentially detect breast cancer, mammography is still the gold standard for early detection.
What are the risk factors for breast cancer?
The main risk factors for breast CA are:
- Family history of a first degree relative
- Previous history of contralateral breast cancer
- Early menarche
- Late menopause
- Nulliparity
- History of endometrial carcinoma
- Increasing age: The probability of developing breast cancer over 10 years starting
- at age 30 is about 0.4%.
- between 40-50 is about 1.5%.
- between 50-60 is about 2.8%.
- between 60-70 is about 3.6%.
Birth control pills and smoking are not risk factors (this is frequently asked on USMLE).
What conditions give rise to false positive suspicion for cancer breast?
Answer
Several benign breast conditions can produce a spiculated density which may be indistinguishable on mammography from carcinoma.
Spiculated mass density has been encountered in:
- Post-biopsy scarring
- Traumatic fat necrosis
- Breast abscess
- Sclerosing adenosis
- Radial scar
Screening mammogram reveals a suspicious lesion for cancer in left breast. No mass is palpable. How would you proceed?
Answer
- Core biopsy of stereotactic or ultrasound guidance; or
- Excision biopsy
- Radiologist performs needle localization procedure first.
- Breast is compressed with holder that has coordinates on the sides, and mammogram is obtained.
- A thin needle is placed in the lesion through coordinates.
- A blue dye is injected at the site.
- A thin hooked wire is passed to the lesion where it gets fixed.
- The needle is withdrawn leaving the wire in place.
- Surgeon removes the tissue around the wire tip.
- The biopsy specimen is x-rayed to make sure that the suspicious lesion was removed.
Image Atlas for Mammography
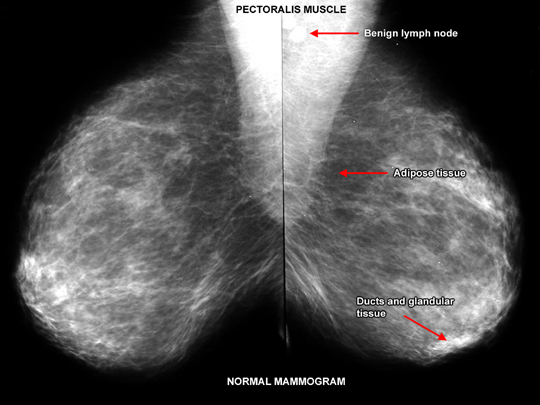
Normal Mammogram
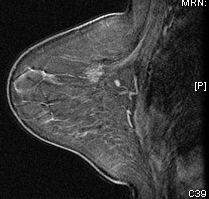
MR Mammogram
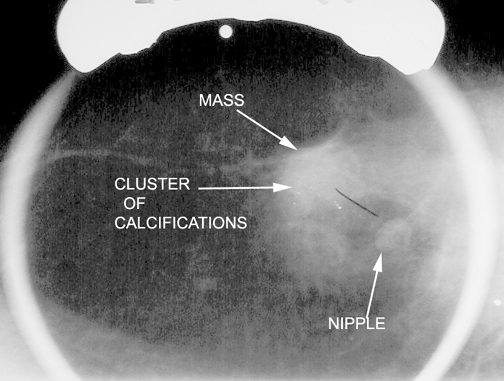
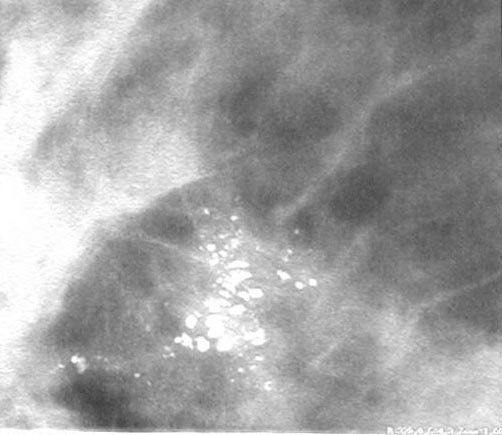
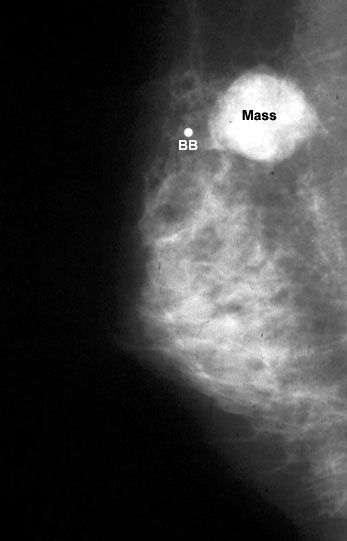
Smooth mass is infiltrating ductal carcinoma medullary type .
THe BB indicates that it is palpable.
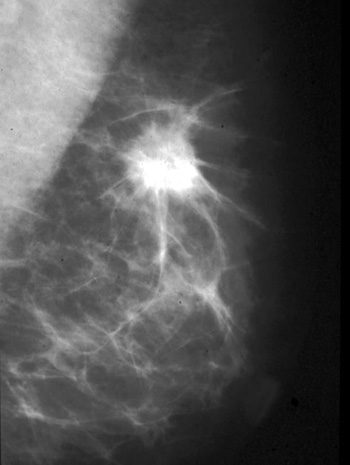
Spiculated mass in upper breast indicating infiltrative ductal carcinoma.
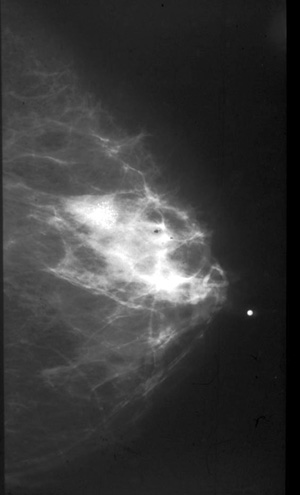
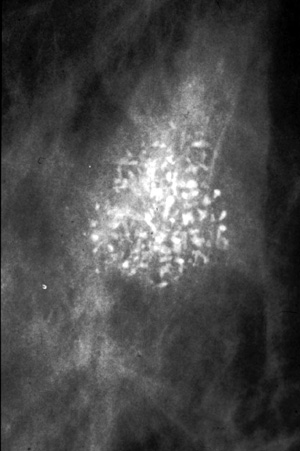
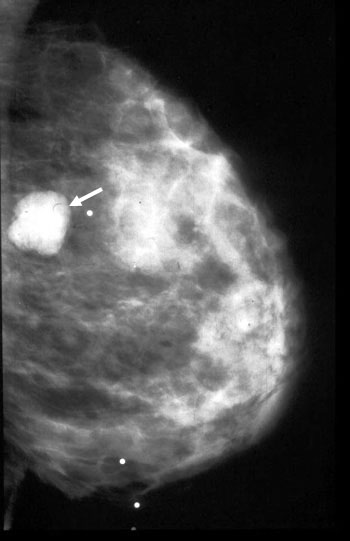
Fibroadenoma
35 year old:
Palpable smooth benign type mass.
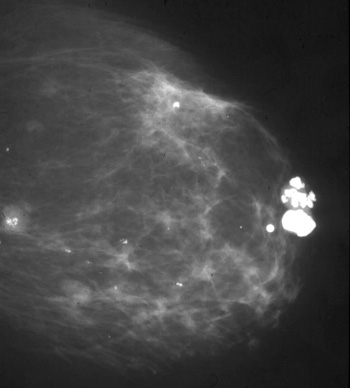
Fibroadenoma
64 year old:
Palpable well delineated mass with irregular "pocorn" calcification.
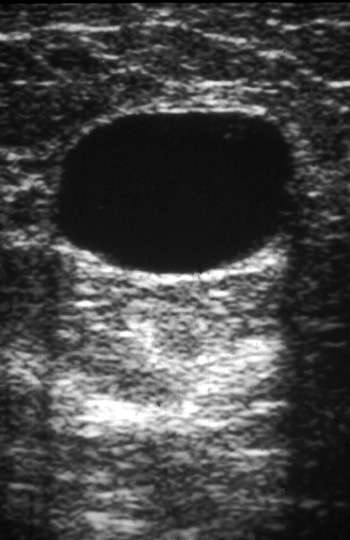
Ultrasound
Cyst
Smooth anechoic mass with enhanced through transmission.
White echoes posterior to cyst.
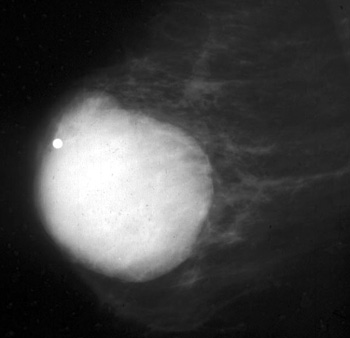
Mammogram
Cyst
Smooth benign type palpable mass.