Ovarian Torsion
by
Molly Jonna, MS4 and Jennifer Lim-Dunham, M.D.
What are the imaging findings in ovarian torsion?
Ovarian torsion refers to the rotation of the ovary resulting in occlusion of the ovarian artery and/or vein and it is the most common gynecologic surgical emergency. Listed below are the main imaging findings in ovarian torsion that can be seen with US, CT, and MRI.
- Ultrasound
- Ovarian enlargement, secondary to impaired venous and lymphatic drainage is the most common sonographic finding.
- The ovary usually contains several immature follicles along its periphery, which are displaced away from the center by edema (string of pearls sign).
- On color and waveform Doppler sonograms one may see little to no intra-ovarian venous flow and sometimes absent arterial flow.
- Normal vascularity on Doppler does not exclude torsion because the torsion may be intermittent or the ovary can be fed by a dual blood supply from both ovarian and uterine arteries.
- Occasionally, the twisted pedicle of the affected ovary can be recognized as a “whirlpool sign.” A twisted pedicle is a relatively specific sign for ovarian torsion.
- An underlying ovarian lesion such as cyst or tumor often predisposes the ovary to torsion
A heterogeneous appearance of the ovarian stroma is sometimes seen and is due to edema and hemorrhage.
- Free pelvic fluid is seen in over 80% of cases
- CT
- On exam torsion appears as an enlarged ovary with a possible underlying ovarian lesion, and it may appear in an abnormal location.
- Lack of enhancement may be seen after the administration of IV contrast
- One may also see surrounding fat stranding, edema, coiled ovarian vessels, and free fluid
- MRI
- MRI findings consistent with ovarian torsion include an enlarged, edematous ovary in an abnormal location.
- With contrast enhancement, the coiled ovarian vessels may be visualized with the “whirlpool” sign.
What are the useful imaging modalities in evaluating ovarian torsion? What is the utility of each procedure?
- Ultrasonography
- Ultrasonography with color and waveform Doppler analysis is the imaging method of choice in suspected cases of ovarian torsion. Both transvaginal and transabdominal pelvic ultrasound should be obtained.
- It can show morphologic and physiologic changes in the ovary and can help determine whether blood flow is impaired.
- This can help predict viability of adnexal structures.
- Normal Doppler imaging, however, does not exclude the diagnosis
- Torsion of the right ovary can be mistaken for appendicitis, and US may help differentiate between the two
- Both ovaries should always be scanned and comparison made between the symptomatic and asymptomatic sides.
- CT/MRI
- Rarely, CT or MRI is needed to make a definitive diagnosis when ultrasonographic findings are non-diagnostic.
- Although CT may demonstrate an enlarged ovary and adnexal masses, it is unable to evaluate the presence or absence of blood flow to the involved ovary.
- In cases of diagnostic uncertainty, however, CT may be useful in ruling out other possible causes of lower abdominal pain.
- Additionally, CT can exclude the presence of a pelvic mass, thereby greatly enhancing the clinician’s ability to rule out torsion.
- MRI is usually not the imaging modality of choice, as more urgent evaluation is needed.
Appropriateness Criteria:
The American College of Radiology has developed Appropriateness Criteria which are evidence-based guidelines that assist physicians in making the most appropriate imaging decisions for a wide variety of clinical conditions.
According to the Appropriateness Criteria for acute pelvic pain in the reproductive age female, both transvaginal and transabdominal pelvic ultrasonography should be inItial studies with Doppler used as an adjunct. If ultrasound is inconclusive or non-diagnostic, an MRI of the abdomen and pelvis can be performed. CT is not recommended due to radiation risk.
Appropriateness Criteria for clinically suspected adnexal mass is similar in that transvaginal and transabdominal ultrasonography with Doppler is the test of choice. Links to the criteria can be found below.
Link to women’s imaging criteria:
http://www.acr.org/Quality-Safety/Appropriateness-Criteria/Diagnostic/Womens-Imaging
Link to imaging criteria for acute pelvic pain in the reproductive age group:
http://www.acr.org/~/media/ACR/Documents/AppCriteria/Diagnostic/AcutePelvicPainReproductiveAgeGroup.pdf
Link to imaging criteria for clinically suspected adnexal mass:
http://www.acr.org/~/media/ACR/Documents/AppCriteria/Diagnostic/ClinicallySuspectedAdnexalMass.pdf
What is the clinical setting when you will consider ovarian torsion?
- Sudden onset of sharp and usually unilateral lower abdominal pain or pelvic pain (90%)
- Nausea and vomiting (47-70%)
- A unilateral, tender adnexal mass (86-95%)
- Fever and vaginal bleeding are uncommon (2-20% and 4%, respectively)
- Abnormal genital tract bleeding (4%)
What are risk factors for developing ovarian torsion?
- Torsion of the ovary usually occurs with torsion of the fallopian tube as well on their shared vascular pedicle around the broad ligament.
- Pathologically enlarged ovaries (more than 6 cm) may alter the position of the fallopian tube and allow twisting to occur
- Ovarian masses such as tumors or cysts are risk factors.
- Since many of these masses are associated with the reproductive cycle or reproductive hormones (eg, corpus luteum, ovulation induction), the risk of torsion is increased in women of reproductive age, during pregnancy, and in women undergoing ovulation induction for treatment of infertility.
- In pregnancy, torsion is probably secondary to ovarian enlargement in combination with laxity of the supporting tissues of the ovary.
- Torsion can also occur due to an enlarged corpus luteum in pregnancy
- Increased length of the ovarian ligaments is a risk factor
- Torsion of a normal ovary more commonly occurs in young children with developmental abnormalities, such as excessively long fallopian tubes or an absent mesosalpinx.
Take Home Points:
- Ovarian torsion refers to the complete or partial rotation of the ovary on its ligamentous supports, often resulting in ischemia. It is one of the most common gynecologic emergencies.
- The primary risk factor for ovarian torsion is an ovarian mass.
- The classic presentation of ovarian torsion is the acute onset of pelvic pain
- Pelvic ultrasound with color and waveform Doppler is the first line imaging study for patients with suspected ovarian torsion. Classic findings are an enlarged ovary with peripheral follicles and decreased intra-ovarian blood flow.
Imaging
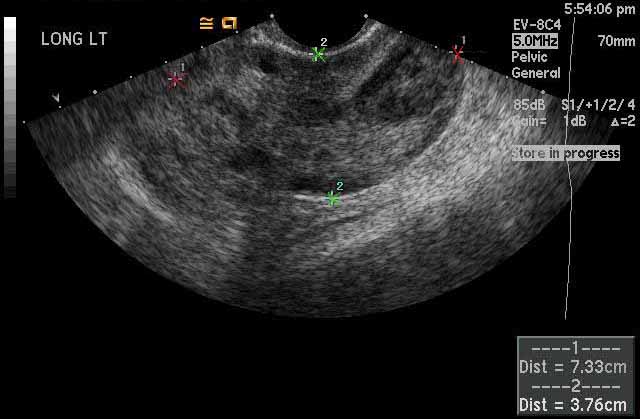 |
Image 1
Left ovarian torsion. The left ovary, marked by the calipers, measures up to 7.3 cm and is abnormally enlarged which is a characteristic feature of ovarian torsion. The normal ovarian size for a woman of childbearing age is 3-5 cm in length. |
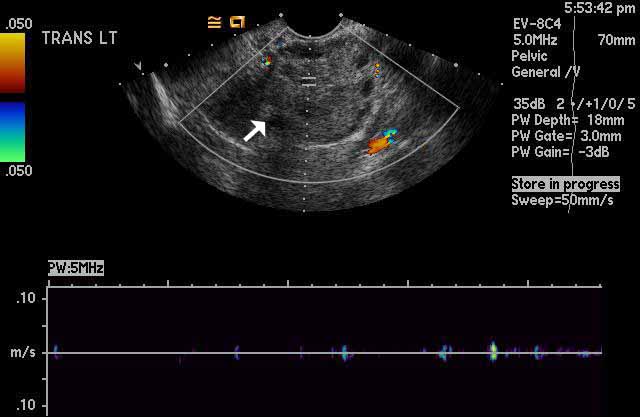 |
Image 2
Left ovarian torsion. Color Doppler ultrasound imaging shows absence of normal intra-ovarian color flow in the left ovary, white arrow, which indicates lack of vascularity and presence of torsion. The graph at the bottom of the image shows lack of normal Doppler waveform tracings, again indicating torsion. |
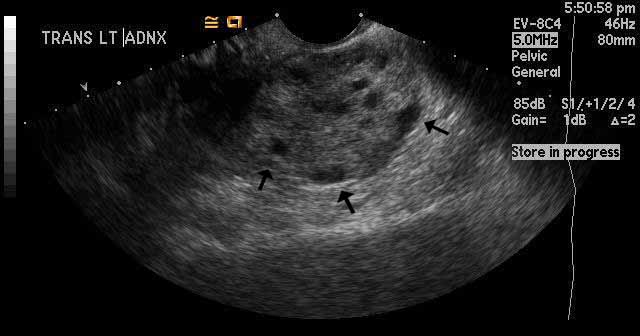 |
Image 3
Left ovarian torsion. The black arrows are pointing toward hypoechoic oval structures along the edge of the left ovary. These represent multiple, prominent, peripheral follicles. This is a classic finding in ovarian torsion. |
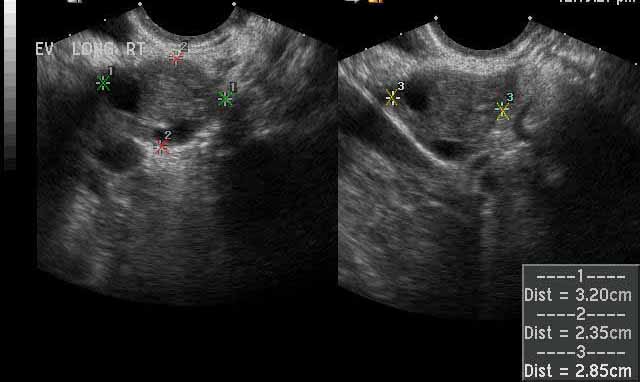 |
Image 4
Normal right ovary for comparison. In contrast to the enlarged left ovary seen in ovarian torsion, these images show a normal sized right ovary, which is marked by the calipers and which measures a maximum of 3.2 cm. |
 |
Image 5
Normal right ovary for comparison. Areas of color signal seen by color Doppler ultrasound within the right ovary represent normal blood vessels and indicate normal blood flow. At the bottom of the image, a normal Doppler waveform tracing showing pulsatile arterial flow confirms presence of blood flow. |
Helpful Links with Additional Imaging:
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2026938-workup#aw2aab6b5b2
- http://www.med-ed.virginia.edu/courses/rad/edus/pelvic1.html
- http://radiopaedia.org/search?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=ovarian+torsion&scope=all
References:
- Sung, R. E., Jae, B. Y., Seung, J. E., Jung, J. I., Byung, C. G., Bum, K. S., Hyun, K., & Jae, L. M. (2002). Ct and mr imaging features of adnexal torsion. RadioGraphics, 22(2), 283-294. Retrieved from http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/pdf/10.1148/radiographics.22.2.g02mr02283
- Chang, H. C., Bhatt, S., & Dogra, V. S. (2008). Pearls and pitfalls in diagnosis of ovarian torsion. RadioGraphics, 28(5), 1355-1368. Retrieved from http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/pdf/10.1148/rg.285075130
- Growden, W. B., & Laufer, M. R. (2013). Ovarian and fallopian tube torsion. In S. Falk, H. Sharp & D. Levine (Eds.), UpToDate. Retrieved from
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/ovarian-and-fallopian-tube-torsion?detectedLanguage=en&source=search_result&search=ovarian+torsion&selectedTitle=1~48&provider=noProvider
12.17.13




