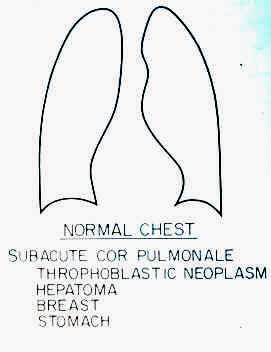
Subacute Cor Pulmonale
- This form of presentation occurs when small subliminal tumor
deposits obstruct a sufficient cross section of the pulmonary vascular
bed.
- The spectrum of pulmonary symptoms is identically to
thromboembolism.
- Patients are in prolonged respiratory distress with
normal chest x-ray, and with or without signs of pulmonary
hypertension.
- Choriocarcinoma, hepatoma, breast and stomach tumors
account for most of the primaries with such presentation.
- This entity should be considered in a female with severe
respiratory distress with a history of recent abortion or delivery
chorionic gonadotropin levels are high.
- When recognized, chemotherapy offers a favorable prognosis in
patients with choriocarcinoma.
- Prognosis is poor with other primary malignancies.
|
 |